Case
A 68 y/o man with a history of kidney transplantation on Tacrolimus and prednisone treatment.
Several months prior to his presentation he underwent excision of a Rt temple skin lesion by a plastic surgeon. Pathology revealed a 4 mm SCC with evidence of PNI and free surgical margins. No further treatment or follow-up was recommended.
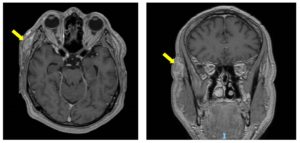
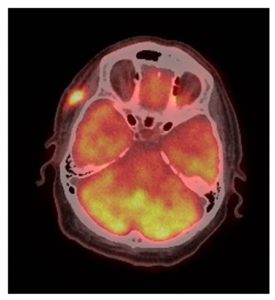
The patient presents now after noticing a weakness of Rt eyebrow for the last two months. He was seen at the Ophthalmology clinic and diagnosed with complete paralysis of the Rt temporal branch of CN-VII. In addition, there was a 2 cm firm subcutaneous painless mass on the Rt temple, deep to the surgical scar. Biopsy of the Rt temple lesion showed SCC. The patient was then referred to the head and neck clinic for further evaluation and treatment. There were no additional findings on physical examination and imaging studies did not show evidence of regional or distant disease (Figures 1, 2).
Risk of recurrence or metastases
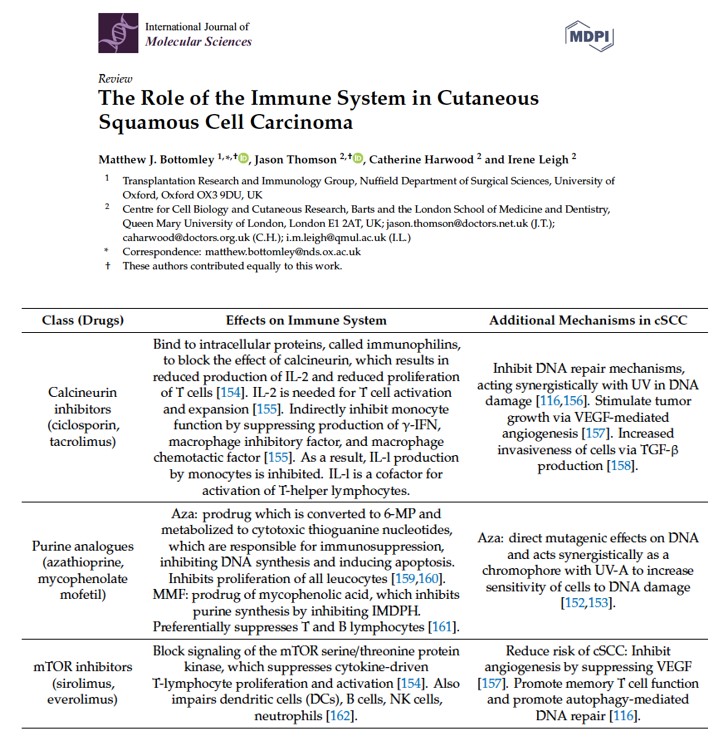
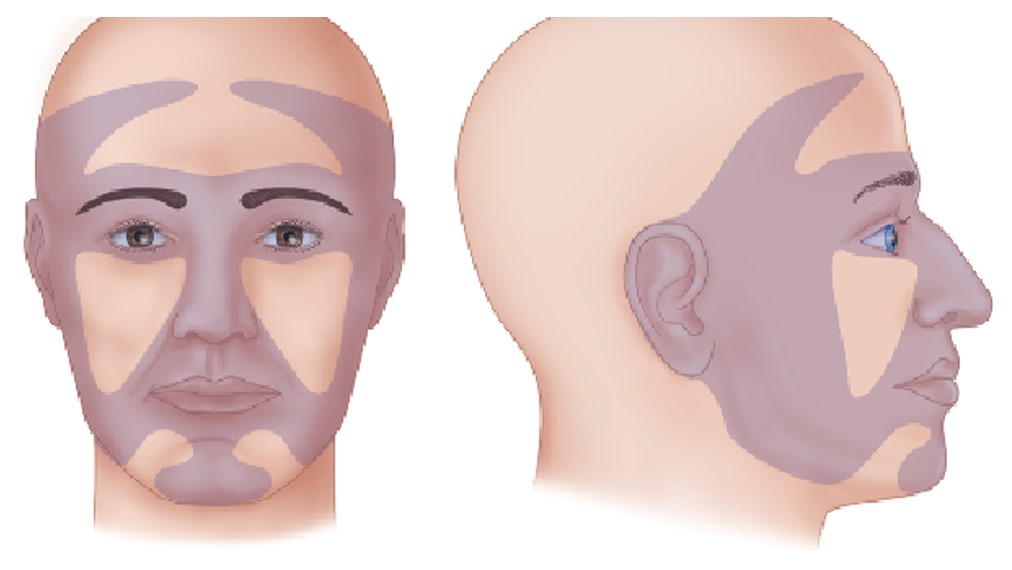
The above case depicts a patient with a high risk for disease recurrence and/or metastases due to chronic immunosuppression. A recent review summarizes the role of the immune system in cutaneous SCC (Figure 3). In this paper the authors illustrate the effect of immunosuppressive drugs on several carcinogenic mechanisms including DNA repair, synergism with UV-related DNA damage, angiogenesis and invasiveness. The NCCN guidelines address the group of high-risk patients with skin SCC and specify the risk factors that warrant close follow-up. Pay attention to “Area H” that includes the “Mask areas” of the face and is considered a high-risk feature (Figure 4).
Management
Every attempt should be made to achieve complete excision of the primary lesion with negative margins. Modification or reduction of immunosuppression should be considered and consulting the appropriate discipline (nephrologist, hepatologist etc.) is strongly encouraged. Adjuvant radiation may be recommended in cases of perineural involvement of large nerves. However, it should be noted that the definition of large nerves by AJCC 8th edition for skin SCC of the head and neck is above 0.1 mm and most nerves deep to the dermis are above 0.1 mm. Moreover, the survival benefit of adjuvant radiation following complete resection of the primary lesion remains unclear (Figure 5).
Outcomes
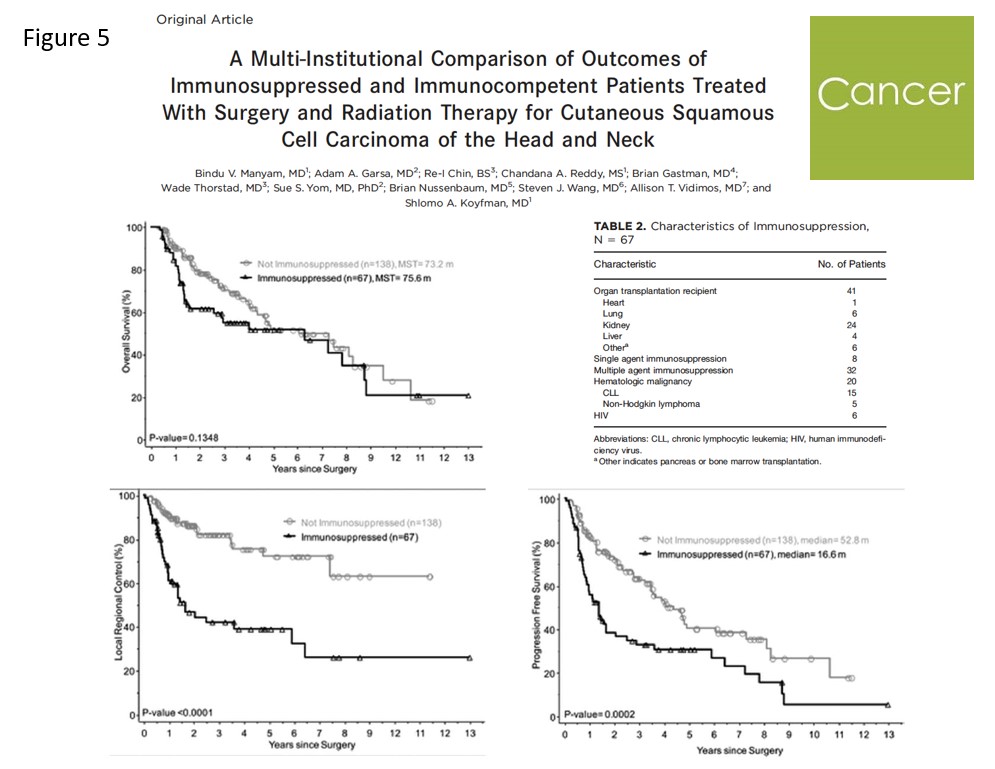
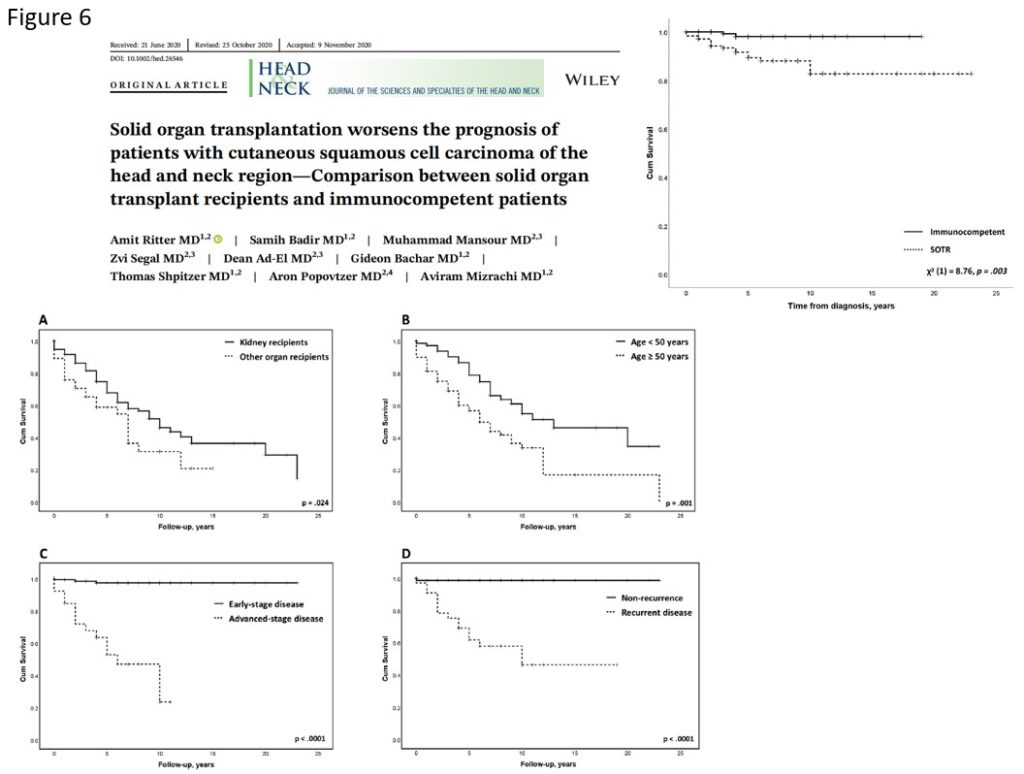
Several studies addressed the differences in survival outcomes between immunosuppressed and immunocompetent patients with skin SCC. A recent multi-center study reported on 67 immunosuppressed patients, most of them solid organ recipients, and compared them with 138 immunocompetent patients (Figure 8). They found better progression free survival and locoregional control in the immunocompetent patients group. However, no difference in overall survival between the two groups was noted. Another study by Ritter et al. compared 177 solid organ recipients with 177 immunocompetent patients with skin SCC. They found a significantly higher recurrence rate and worse overall survival in the solid organ recipients group (Figure 6).
Checkpoint inhibitors
Immunocompromised patients have been traditionally excluded from the major clinical trials on checkpoint inhibitors. Solid organ recipients and patients with chronic viral infections (HIV, HBV, HCV) are considered poor candidates for checkpoint inhibitors due to the risk of allograft rejection and disease flare-up respectively. A multi-center European study reported on 46 patients treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 agents. Of them 6 were solid organ recipients and the remaining had chronic viral infections. They concluded that while patients with chronic viral infection may be safely treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 drugs, in solid organ recipients the risk of allograft rejection needs to be carefully weighed against the benefit of immunotherapy (Figure 7).

“CONCLUSION: Patients with HIV or hepatitus B/C infection treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy may respond to treatment without increased toxicity. Given the risk of graft rejection in solid organ transplant patients and also the potential for response, the role of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy needs to be carefully considered.”
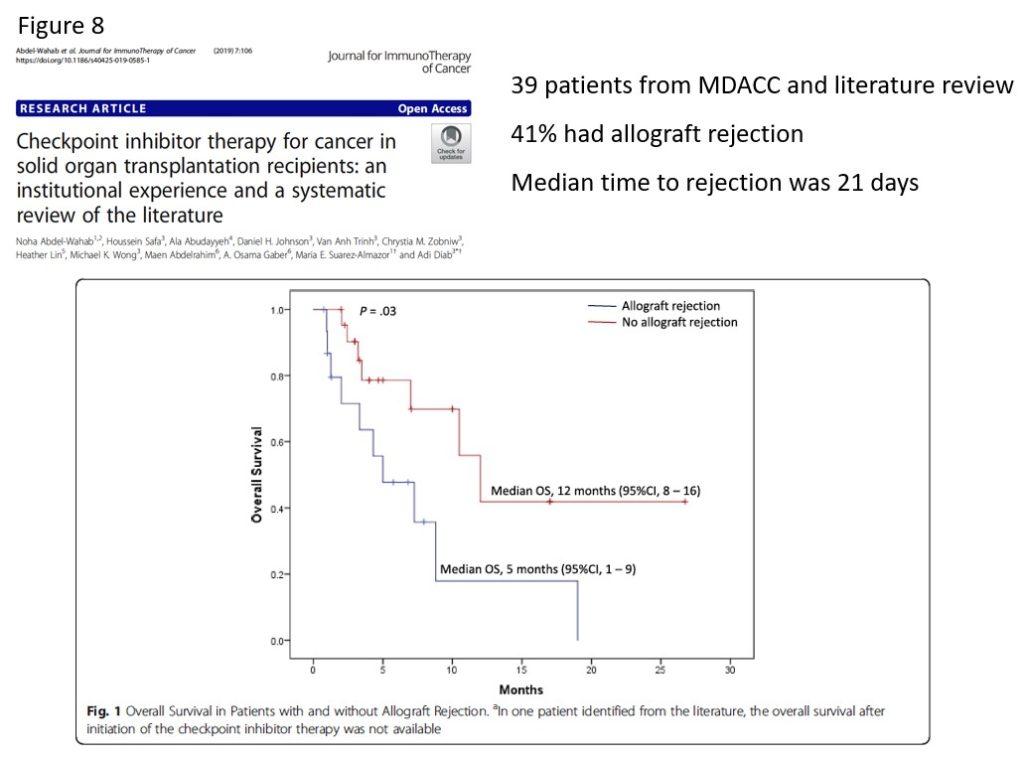
Another study from MD Anderson Cancer Center reported on 37 solid organ recipients treated with checkpoint inhibitors. They found that 41% of patients experienced allograft rejection with a median time to rejection of 21 days from the initiation of immunotherapy. Furthermore, patients with allograft rejection had a significantly worse overall survival (Figure 8).
There is certainly a need for prospective trials in order to optimize the use of checkpoint inhibitors in immunosuppressed patients. A recently opened trial is enrolling kidney transplant recipients with advanced cancers, with an aim to treat them with Tacrolimus, Nivolumab and Ipilimumab. Additional details on this topic and the trial can be found in the following link:
References
- Bottomley MJ, Thomson J, Harwood C, Leigh I. The Role of the Immune System in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 24;20(8):2009. doi: 10.3390/ijms20082009. PMID: 31022866; PMCID: PMC6515307.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Squamous Cell Skin Cancer (Version 2.2020). https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/squamous.pdf
- Manyam BV, Garsa AA, Chin RI, Reddy CA, Gastman B, Thorstad W, Yom SS, Nussenbaum B, Wang SJ, Vidimos AT, Koyfman SA. A multi-institutional comparison of outcomes of immunosuppressed and immunocompetent patients treated with surgery and radiation therapy for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer. 2017 Jun 1;123(11):2054-2060. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30601. Epub 2017 Feb 7. PMID: 28171708.
- Ritter A, Badir S, Mansour M, Segal Z, Ad-El D, Bachar G, Shpitzer T, Popovtzer A, Mizrachi A. Solid organ transplantation worsens the prognosis of patients with cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck region-Comparison between solid organ transplant recipients and immunocompetent patients. Head Neck. 2020 Nov 27. doi: 10.1002/hed.26546. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33247523.
- Tio M, Rai R, Ezeoke OM, McQuade JL, Zimmer L, Khoo C, Park JJ, Spain L, Turajlic S, Ardolino L, Yip D, Goldinger SM, Cohen JV, Millward M, Atkinson V, Kane AY, Ascierto PA, Garbe C, Gutzmer R, Johnson DB, Rizvi HA, Joshua AM, Hellmann MD, Long GV, Menzies AM. Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy in patients with solid organ transplant, HIV or hepatitis B/C infection. Eur J Cancer. 2018 Nov;104:137-144. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2018.09.017. Epub 2018 Oct 20. PMID: 30347289.
- Abdel-Wahab N, Safa H, Abudayyeh A, Johnson DH, Trinh VA, Zobniw CM, Lin H, Wong MK, Abdelrahim M, Gaber AO, Suarez-Almazor ME, Diab A. Checkpoint inhibitor therapy for cancer in solid organ transplantation recipients: an institutional experience and a systematic review of the literature. J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Apr 16;7(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0585-1. Erratum in: J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Jun 24;7(1):158. PMID: 30992053; PMCID: PMC6469201.


 Myers’ Family Summer Travel Fellowship in Otolaryngology Application is Open
Myers’ Family Summer Travel Fellowship in Otolaryngology Application is Open